An Introduction to Azithromycin and its Role in Fighting Bacterial Infections
Azithromycin is a popular antibiotic that is prescribed by doctors to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections. It belongs to the class of macrolide antibiotics and works by stopping the growth of bacteria, ultimately helping our body's immune system to eliminate the infection. In this article, we will explore how azithromycin works, discuss its effectiveness in treating various types of bacterial infections, and highlight the potential side effects and precautions one should take when using this medication. So, let's dive in!
The Science Behind Azithromycin's Bacterial Inhibition
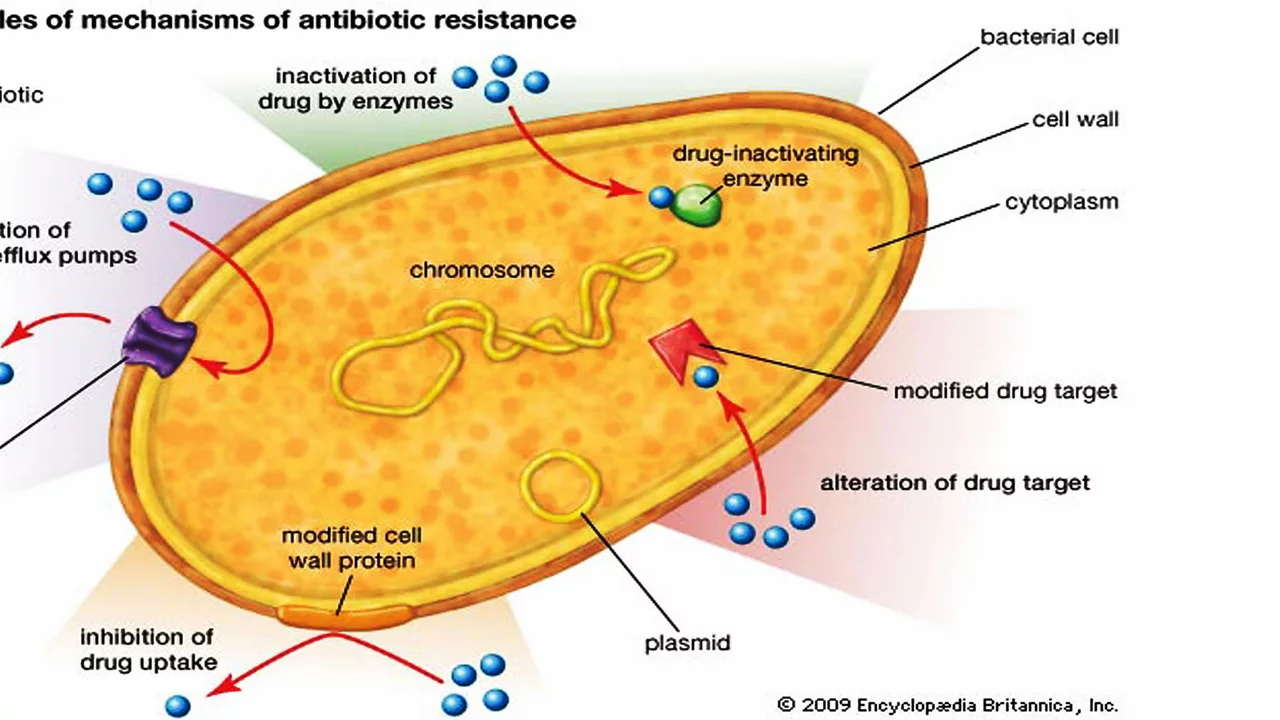
As a macrolide antibiotic, azithromycin works by inhibiting the protein synthesis of bacteria, effectively stopping their growth and multiplication. It does this by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome, which is responsible for creating new proteins. This binding action prevents the bacteria from producing essential proteins they need to grow and reproduce.
The result is a weakened bacterial population that is susceptible to our body's natural defense mechanisms. As the immune system attacks and eliminates the bacteria, the infection begins to clear up, and the symptoms of the infection start to subside.
Common Bacterial Infections Treated with Azithromycin
Azithromycin is prescribed to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted infections. Some of the common conditions that can be treated with this antibiotic include:
- Strep throat
- Pneumonia
- Bronchitis
- Sinusitis
- Ear infections
- Skin infections such as cellulitis or impetigo
- Sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea
It is important to note that azithromycin is not effective against viral infections, such as the common cold or flu. Your doctor will determine if azithromycin is the right antibiotic to treat your particular infection based on your symptoms and medical history.
How to Properly Use Azithromycin for Maximum Effectiveness
To ensure that azithromycin effectively treats your bacterial infection, it is essential to follow your doctor's instructions and complete the entire course of treatment. Skipping doses or stopping the medication too soon can lead to the bacteria becoming resistant to the antibiotic, making the infection harder to treat in the future.
Azithromycin is typically taken once daily, with or without food. However, it is best to take it at the same time each day to maintain consistent levels of the medication in your body. If you experience stomach upset, taking the medication with food may help alleviate this side effect. Be sure to drink plenty of fluids while taking azithromycin to help flush the bacteria from your system.
Potential Side Effects of Azithromycin
As with any medication, there are potential side effects associated with azithromycin. While most people tolerate the medication well, it is essential to be aware of the possible side effects and to discuss them with your doctor if they become severe or persistent. Some common side effects include:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Stomach pain or cramping
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Changes in taste
Rare but serious side effects can also occur, such as an irregular heartbeat, severe allergic reactions, or liver problems. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Precautions to Take While Using Azithromycin
Before starting azithromycin, it is essential to inform your doctor about any allergies you may have, especially to macrolide antibiotics or any other medications. Additionally, inform your doctor about any pre-existing medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, heart problems, or a history of a specific type of irregular heartbeat known as long QT syndrome.
It is also important to discuss any other medications or supplements you are currently taking, as they may interact with azithromycin. Some examples of medications that may interact with azithromycin include antacids containing aluminum or magnesium, blood thinners, or certain live bacterial vaccines.
Conclusion: Azithromycin as an Effective Weapon Against Bacterial Infections
In summary, azithromycin is a powerful antibiotic that is commonly prescribed to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. By inhibiting the growth and reproduction of bacteria, it allows our immune system to effectively eliminate the infection. As with any medication, it is essential to follow your doctor's instructions and be aware of potential side effects and precautions to ensure the safe and effective use of azithromycin. With the proper use and monitoring, azithromycin can help you overcome bacterial infections and get back to feeling your best.

Comments
Edward Brown
Think about the invisible war inside our cells the bacteria multiply like hidden invaders and azithromycin steps in as a silent soldier binding that ribosomal gear It stops the protein factory and leaves the bugs defenseless
June 18, 2023 AT 20:37
ALBERT HENDERSHOT JR.
Great overview! It's important to remember that completing the full course is essential for preventing resistance. Keeping a consistent dosing schedule helps maintain therapeutic levels, and staying hydrated supports the drug's distribution 😊
June 18, 2023 AT 21:27
Suzanne Carawan
Oh sure, because the world needed another fancy name for a pill that just tells bacteria to stop working. Who cares about the 50S ribosome when you can just blame the infection on “not taking it properly”?
June 18, 2023 AT 22:33
Kala Rani
Azithro is just a pill not a miracle.
June 18, 2023 AT 23:40
Donal Hinely
Listen up folks, azithromycin isn’t some meek herbivore – it’s a full‑blown beast that crashes the bacterial party like a wrecking ball. It latches onto that 50S subunit and throws a molecular punch that shatters the protein synthesis chain. The result? Bacterial cells go from hyper‑active to dead‑beat faster than you can say “antibiotic resistance”. So when your doc hands you this drug, know you’ve got a heavyweight champion in your bloodstream, ready to KO any nasty germ that dares to show up.
June 19, 2023 AT 00:47
christine badilla
OMG I was like totally blown away by that description! My head is spinning from all the metaphor fireworks, but yeah it sounds like a bacterial apocalypse in a bottle.
June 19, 2023 AT 01:05
Octavia Clahar
Honestly, while the description sounds exciting, it’s a bit over‑the‑top. The drug does its job, but let’s not glorify antibiotics as if they’re invincible heroes. Responsible use is key.
June 19, 2023 AT 01:55
eko lennon
Azithromycin, despite its seemingly simple pill form, embodies a cascade of biochemical events that merit deeper appreciation.
When administered, the drug diffuses into tissues and attains concentrations that exceed plasma levels, a property that makes it especially effective for intracellular pathogens.
Its affinity for the 50S ribosomal subunit is not merely a static lock‑and‑key interaction; it induces conformational changes that stall the translocation step of protein elongation.
By freezing the ribosome mid‑action, the bacterium is denied the synthesis of essential enzymes and structural proteins, effectively halting its growth cycle.
This bacteriostatic effect leverages the patient’s own immune defenses, allowing phagocytes and other innate cells to clear the crippled microbes.
The pharmacokinetic profile, characterized by a long half‑life of approximately 68 hours, permits once‑daily dosing and, in many cases, a shortened treatment duration compared to older macrolides.
However, this prolonged exposure also raises concerns about selective pressure, potentially fostering resistant strains if the regimen is misused.
Clinicians must therefore balance the convenience of a three‑day course against the ecological impact on the microbiome.
Moreover, azithromycin’s interaction with the cardiac QT interval, though rare, necessitates vigilance in patients with pre‑existing arrhythmias.
Drug‑drug interactions, such as with antacids containing aluminum or magnesium, can diminish absorption, underscoring the importance of timing relative to meals.
From a therapeutic standpoint, its efficacy against atypical organisms like Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Chlamydia trachomatis expands its utility beyond classic Gram‑positive infections.
Yet, it remains impotent against viral pathogens, a fact that is sometimes lost in the public’s misunderstanding of antibiotics.
The side‑effect profile, ranging from mild gastrointestinal upset to the occasional hepatotoxic event, reflects the balance between benefit and risk that all antimicrobials share.
Patient education, therefore, becomes a cornerstone of successful therapy, ensuring adherence and mitigating adverse outcomes.
In the grand scheme, azithromycin represents a powerful tool in our antimicrobial arsenal, but like any tool, it demands respect, precision, and judicious application.
When wielded responsibly, it can turn the tide of infection without sowing the seeds of future resistance.
June 19, 2023 AT 03:01
Sunita Basnet
Spot on the deep dive highlights key pharmacodynamics and dosing kinetics great job the synergy between host immunity and drug action really shines keep spreading the knowledge
June 19, 2023 AT 03:18
Melody Barton
Good job on covering the basics, but remember to stress the importance of finishing the whole prescription. Cutting short can lead to nasty resistant bugs.
June 19, 2023 AT 04:25
Justin Scherer
Exactly, finishing the full course is the safest way to make sure the infection is fully cleared and to protect the community.
June 19, 2023 AT 04:41
Pamela Clark
Wow, another groundbreaking article on antibiotics that we’ve all read a thousand times. Can’t wait for the sequel on why water is wet.
June 19, 2023 AT 05:48